

Synapsis: Synapsis ensures the proper segregation of homologous chromosomes and allows the recombination through crossing over.Ĭrossing Over: Crossing over allows the variations of alleles in a population through genetic recombination. CorrelationĬrossing Over:Crossing over may occur sometimes. CorrespondenceĬrossing Over: Synapsis is followed by crossing over. Synapsis:The pairing of the homologous chromosomes during the prophase 1 of the meiosis 1 is known as the synapsis.Ĭrossing Over:The exchange of the genetic material during synapsis is known as the crossing over. Difference Between Synapsis and Crossing Over Definition The concentration of beneficial genes would be an advantage towards the species. The repeated crossing over allows the genes in that regions to concentrate independently. The genetic variation exerted by crossing over provides a defense against the process called chromosome killer. Function of Crossing OverĬrossing over increases the genetic variation within an offspring. Synthesis-dependent strand annealing (SDSA) is another type of recombination that occurs during synapsis, which allows the exchange of information, but not the physical exchange of DNA pieces.

DNA repair occurs in response to DNA damage, especially double-strand breaks during synapsis. Secondly, the chromosomal cross-over at chiasmata of non-sister chromatids allows the genetic recombination of chromosomes to occur, resulting in new combinations of alleles in the inherited chromosomes. This is called the law of independent assortment, which allows the segregation of maternal and paternal chromosomes in a random nature. First is the independent orientation of the pairs of the homologous chromosomes in the cell equator. During synapsis, genetic variation is allowed in two ways. The major role of synapsis is the recognition of the two homologues by pairing, in order to undergo a successful synapsis. But, sex chromosomes form a single synaptonemal complex at one end of each chromosome. (B) Tomato SCs at the top and two tomato SCs (Crossing over occurs at the marked sites.)Īutosomes form two synaptonemal complexes at the two ends of the chromosome. (A) Lateral view: homologous chromosomes (light blue rods) aligned together by the meshwork of transverse (black lines) and longitudinal (dark blue rods) filaments. A synaptonemal complex is shown in figure 1. Then, the intervening regions of the two chromosomes are connected by synaptonemal complexes, which consist of RNA and proteins. These chromosomal end-membrane complexes are migrated until they find the other homologue to pair with the assistance of the extranuclear cytoskeleton. Mechanism of Synapsisĭuring synapsis, the ends of the individual chromosomes are attached to the nuclear envelope first. It allows the two homologous chromosomes to segregate at the anaphase 1 of meiosis 1. The synapsis occurs at prophase 1 of meiosis 1. The pairing of the two homologous chromosomes during the meiosis is known as synapsis. What is the difference between Synapsis and Crossing Over
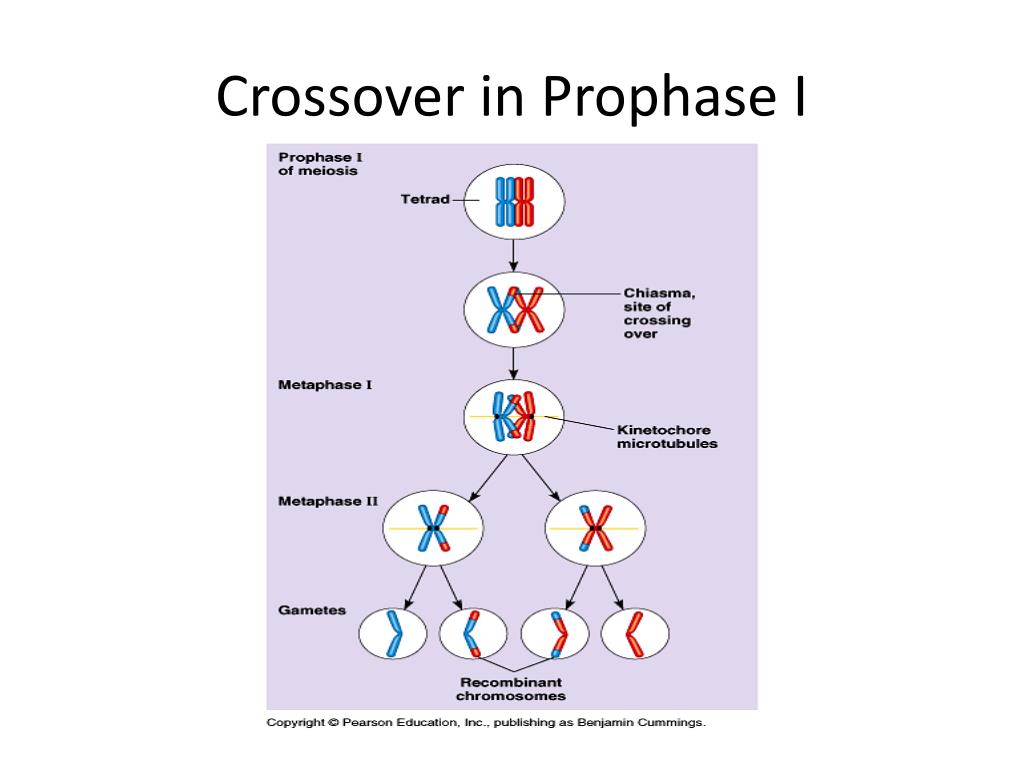
– Definition, Mechanism, Function, Characteristicsģ. The main difference between synapsis and crossing over is that synapsis is the pairing of homologous chromosomes during the prophase 1 of the meiosis 1 whereas crossing over is the exchange of the genetic material during synapsis. Both synapsis and crossing over are important in exerting genetic variation among the individuals by allowing the exchange of genetic material between homologous chromosomes. Meiosis occurs during the production of gametes in order to achieve the sexual reproduction of organisms. Synapsis and crossing over are two events that occur during the chromosome segregation in meiosis 1. Homologous chromosomes contain the same genes, but one copy is derived maternally (from your mother), and the other is derived paternally (from your father).Main Difference – Synapsis vs Crossing Over


 0 kommentar(er)
0 kommentar(er)
